Motorola Surfboard SBG6580’s QoS settings is actually hidden under Wireless > WMM section. However, different compared to some of the routers that already have different setup configurations. You can actually change each of QoS priority settings in SBG6580. However, great freedom comes at a cost, wrong setups can cause your wireless to have serious issues that are hard to diagnose and fix.
Please note that this section have the potential to make your wireless network unuseable, especially if you have multiple Access Points (AP) in your network. However, if you only have 1 single SBG6580 in your house, these setting changes should improve your wifi performance. Consider to have wired connection ready in case our recommendations break your Wireless network completely. We have provided default settings here as well, so that you can have a QoS setting to fall back on in case our recommendations break yours.
For the purpose of this SBG6580 QoS WMM guide. We will provide a screen shot detailing the potential changes that you can make to make your online experience smoother. Then we will give a little background at the end of this post to help you understand more about the QoS parameters.
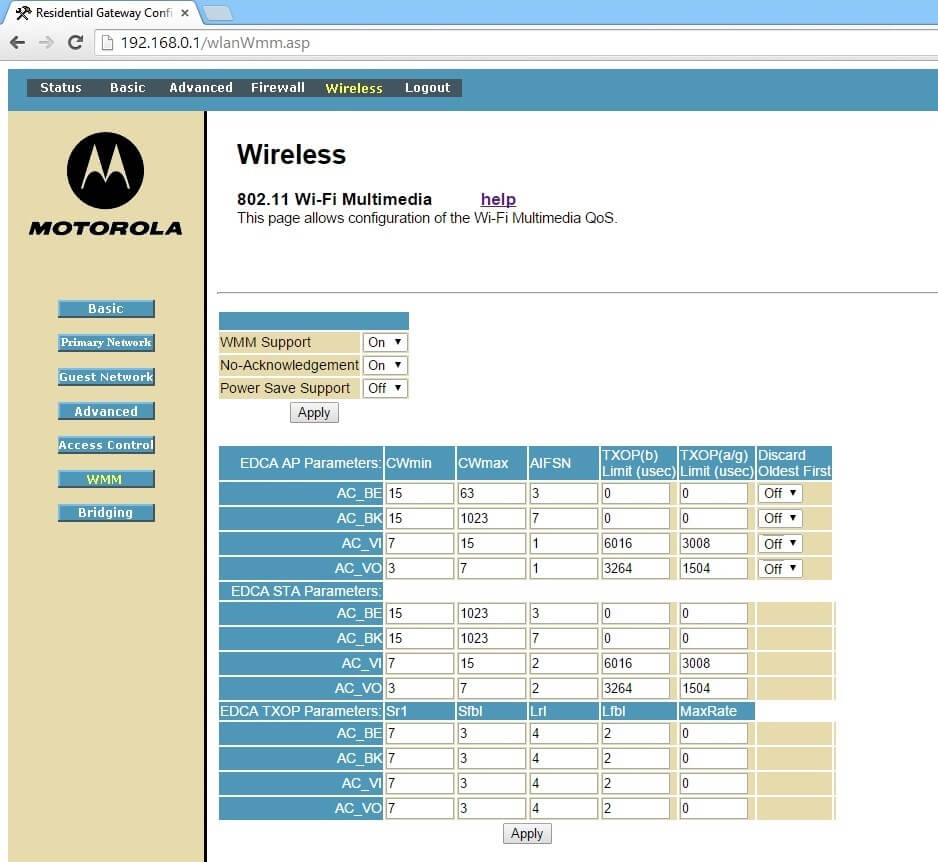
Default WMM QoS Settings
Below is a screen shot of the default configuration in case you ever need to fall back.
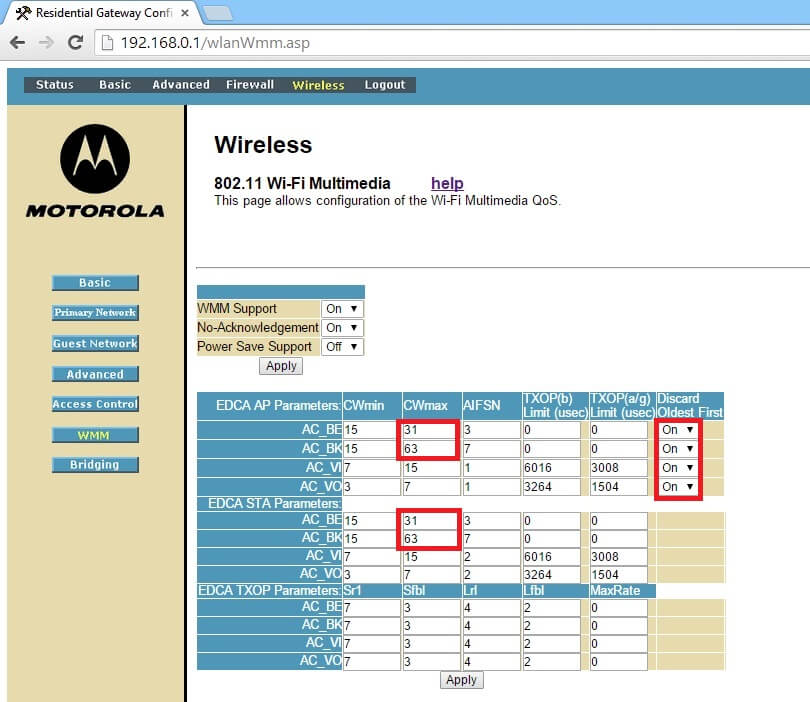
Changes:
1. EDCA AP Parameter: AC_BE CWmax from 63 to 31.
2. EDCA AP Parameter: AC_BK CWmax from 1023 to 63.
3. EDCA STA Parameter: AC_BE CWmax from 1023 to 63.
4. EDCA STA Parameter: AC_BK CWmax from 1023 to 63.
5. Turn on the Discard rule.
SBG6580 WMM QoS Upper Section Configuration
The upper sections for your SBG6580 WMM (QoS) are typically pretty safe to change. Please read our generic WMM settings guide for more information on this part.
WMM Support: On
No-Acknowledgement: On
Power Save Support: Off
SBG6580 WMM QoS Lower Section Configuration
For the QoS parameters to actually take effect in this section, you need to enable WMM settings on the upper section.
Different Type of QoS Data Queues
AC_BE: Data 0 (Best Effort, BE): Medium priority queue, medium throughput and
delay. Most traditional IP data.
AC_BK: Data 1 (Background, BK): Lowest priority queue, high throughput. Bulk
data (Like FTP) that requires maximum throughput and is not time-sensitive.
AC_VI: Data 2 (Video, VI): High priority queue, minimum delay. Time-sensitive
data such as Video and other streaming media.
AC_VO: Data 3 (Voice, VO): Highest priority queue, minimum delay.
Time-sensitive data such as Voice over IP (VoIP).
Random Backoff and Minimum (CWmin) / Maximum (CWmax) Contention Windows
If an access point detects that the medium is in use (busy), it uses the DCF random backoff timer to determine the amount of time to wait before attempting to access a given channel again. Each access point
waits some random period of time between retries.
The wait time is initial a value within a range between Minimum Contention Window and Maximum Contention Window. CWmin to CWmax. The values that you can input is 2^n – 1. For example, you can input 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, …, 1023, and so on.
When you have higher numbers of users, your network gains from having a higher number of waiting time window. Because it lowers the amount of wireless collisions which reduce retransmissions. However, if you have a small network having a high value can slow down your potential speed.
In general, you still want to have a lower value for Video and VO’s because you do want higher priority for those services.
AIFSN
The Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing (AIFs) specifies a wait time (in milliseconds) for data frames. 802.11e uses interframe spaces to regulate which frames get access to available channels and to coordinate wait times for transmission of different types of data. The AIFs ensures that multiple access points do not try sending data at the same time but instead wait until a channel is free.
Valid values for AIFs are 1 through 255. You want to keep this value as low as you can, especially if you have a small network.
For our purposes, keep the setting as the original.
Transmission Opportunity TXOP
The Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) is an interval of time when a WMM client station has the right to initiate transmissions onto the wireless medium.
This value specifies (in milliseconds) the Transmission Opportunity (TXOP) for client stations; that is, the interval of time when a WMM client station has the right to initiate transmissions on the wireless network.
For our purposes, keep the setting as the original.